Stroke Surgery
What is it?
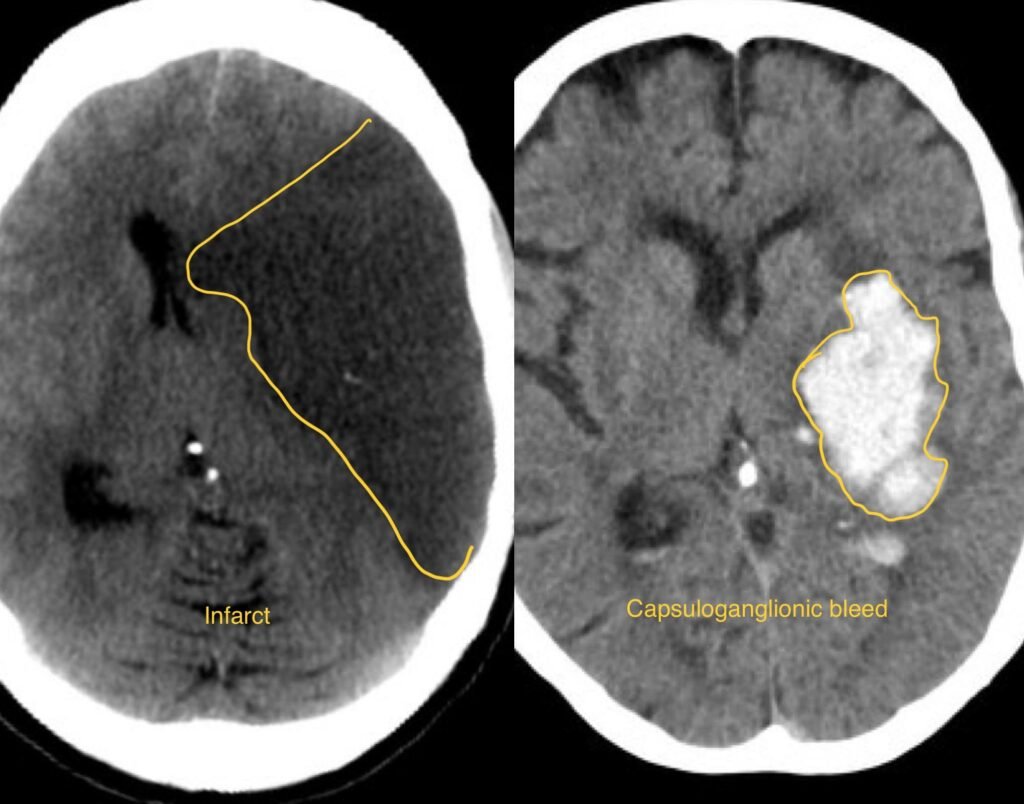
Stroke surgery, also known as cerebrovascular surgery or neurosurgical intervention for stroke, refers to surgical procedures performed to treat acute ischemic strokes or prevent future strokes caused by conditions such as carotid artery disease or intracranial aneurysms. These surgeries aim to restore blood flow to the affected areas of the brain, remove blood clots, repair damaged blood vessels, or prevent further complications.
Symptoms:
Symptoms of stroke can vary depending on the type and location of the stroke but often include sudden onset of:
- Weakness or numbness on one side of the body, particularly in the face, arm, or leg.
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech.
- Vision changes in one or both eyes.
- Severe headache, often described as the worst headache of one’s life, particularly with a sudden onset.
Primary Symptoms:
The primary symptoms of stroke, often referred to as FAST (Face drooping, Arm weakness, Speech difficulty, Time to call emergency services), include:
- Face Drooping: One side of the face may droop or feel numb when the person tries to smile.
- Arm Weakness: One arm may feel weak or numb, and the person may have difficulty raising both arms evenly.
- Speech Difficulty: Speech may be slurred or difficult to understand, and the person may have trouble repeating simple phrases.
- Time to Call Emergency Services: If any of these symptoms occur, it’s essential to call emergency services immediately, as prompt treatment can significantly improve outcomes.
Diagnosis/Treatment:
- Diagnosis of stroke typically involves a thorough neurological examination, medical history, imaging studies such as CT scans or MRI, and blood tests to evaluate blood clotting and other factors.
- Treatment options for stroke depend on the type and cause of the stroke but may include medications such as clot-busting drugs (thrombolytics), procedures to remove blood clots (mechanical thrombectomy), surgery to repair damaged blood vessels or remove plaque buildup (endarterectomy), and rehabilitation therapies such as physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy.
What to Expect After Surgery:
- After stroke surgery, patients can expect a period of recovery, which may involve monitoring in the intensive care unit (ICU) or stroke unit, medication management, and rehabilitation therapies.
- Recovery time varies depending on the type and severity of the stroke, the effectiveness of treatment, and the individual patient’s condition, but most patients can expect to gradually improve over several weeks to months.
- Rehabilitation may include physical therapy to regain strength and mobility, occupational therapy to improve activities of daily living, speech therapy to address communication difficulties, and cognitive therapy to address memory and thinking problems.
Risk & Complications:
- As with any surgery, there are risks associated with stroke surgery, including bleeding, infection, nerve injury, stroke recurrence, and complications related to anesthesia.
- Additionally, there may be a risk of complications specific to the type of surgery performed, such as damage to surrounding brain tissue, blood vessel injury, or incomplete removal of blood clots.
- However, complications are relatively rare, and the benefits of surgery often outweigh the risks, particularly when prompt treatment is essential to minimize brain damage and improve outcomes after a stroke. Early recognition of stroke symptoms and timely intervention can significantly reduce the risk of disability and improve quality of life for stroke survivors.
Brain Treatments
About Dr. Bharat
Dr Bharat Shinde completed his M.Ch Neurosurgery from the National Institute Of Mental Health And Neurosciences (NIMHANS), Bangalore which is an institute of National importance.
