Spinal Deformity
What is it?
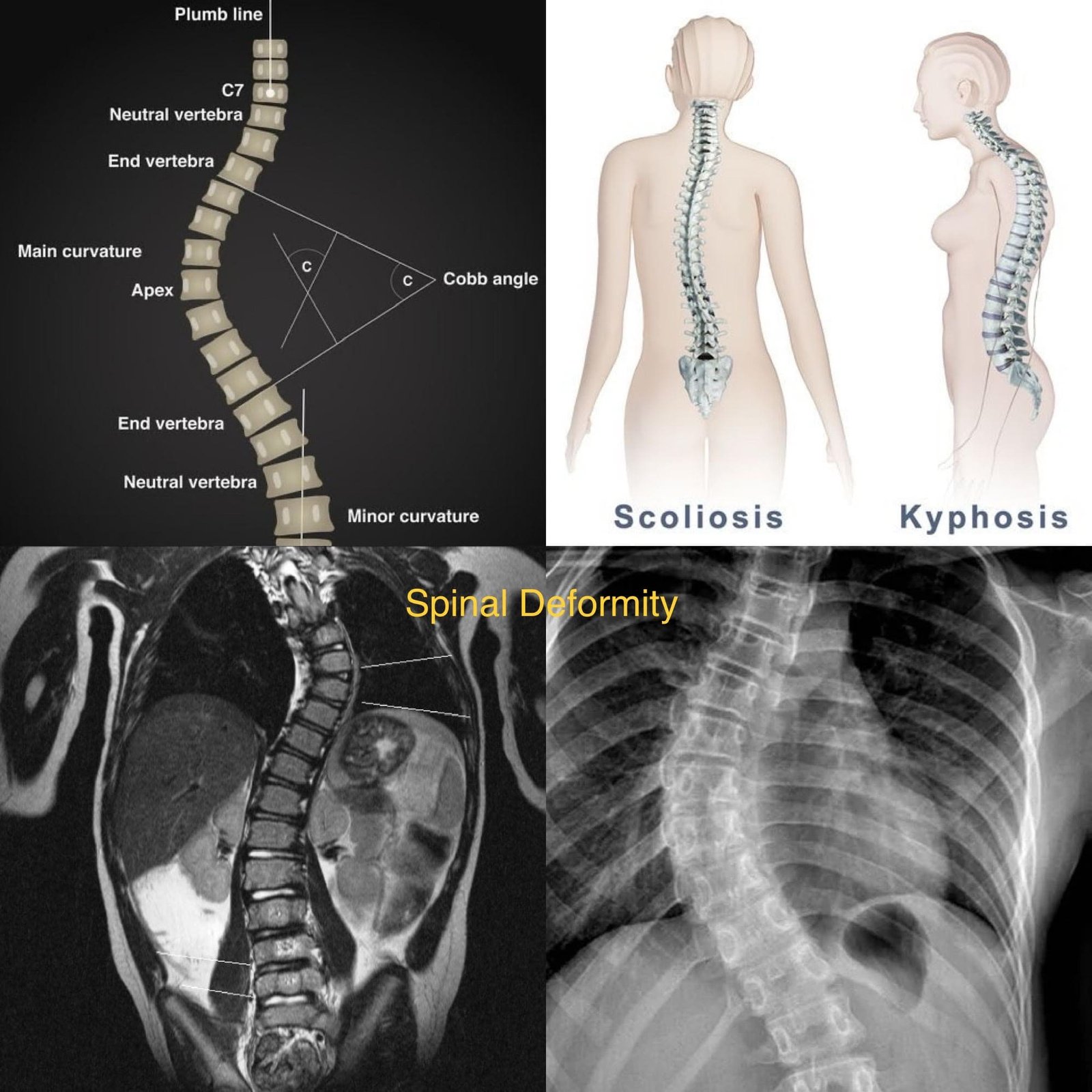
Spinal deformity refers to any abnormal curvature or misalignment of the spine. This can include conditions such as scoliosis (lateral curvature), kyphosis (excessive forward curvature), and lordosis (excessive backward curvature). Spinal deformities can occur in any part of the spine and can be congenital (present at birth) or acquired (developed over time).
Symptoms:
- Symptoms of spinal deformity can vary depending on the type and severity of the deformity.
- Common symptoms may include back pain, stiffness, muscle fatigue, changes in posture, difficulty breathing, and neurological deficits (such as weakness or numbness in the limbs).
Primary Symptoms:
The primary symptoms of spinal deformity may include:
- Visible curvature of the spine, such as a sideways curve (scoliosis), hunchback (kyphosis), or swayback (lordosis).
- Pain or discomfort in the back, particularly with prolonged sitting or standing or with certain movements.
- Changes in posture, such as leaning to one side or having rounded shoulders.
- Difficulty breathing, especially with severe deformities that compress the lungs or chest cavity.
- Neurological deficits, such as weakness, numbness, or tingling in the arms or legs, which may indicate compression of the spinal cord or nerves.
Diagnosis/Treatment:
- Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and imaging studies such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI to evaluate the structure and alignment of the spine.
- Treatment options vary depending on the type and severity of the deformity but may include observation, bracing, physical therapy, medication, or surgery to correct the curvature, relieve symptoms, and prevent progression.
What to Expect After Surgery:
- After surgery for spinal deformity, patients can expect relief from symptoms such as pain, stiffness, and neurological deficits.
- Recovery time varies depending on the type of surgery and the individual patient’s age and overall health, but most patients can expect to gradually improve over several weeks to months.
- Physical therapy may be recommended to help strengthen the muscles supporting the spine and improve mobility and function.
Risk & Complications:
- As with any surgery, there are risks associated with procedures to treat spinal deformity, including infection, bleeding, nerve injury, spinal fluid leakage, and complications related to anesthesia.
- Additionally, there may be a risk of incomplete correction of the deformity, recurrence of symptoms, or complications specific to the surgical technique used.
However, complications are relatively rare, and the benefits of surgery often outweigh the risks, particularly when conservative treatments have failed to provide relief or when there is evidence of progressive spinal deformity or neurological deficits that require surgical intervention.
Spine Treatments
About Dr. Bharat
Dr Bharat Shinde completed his M.Ch Neurosurgery from the National Institute Of Mental Health And Neurosciences (NIMHANS), Bangalore which is an institute of National importance.
