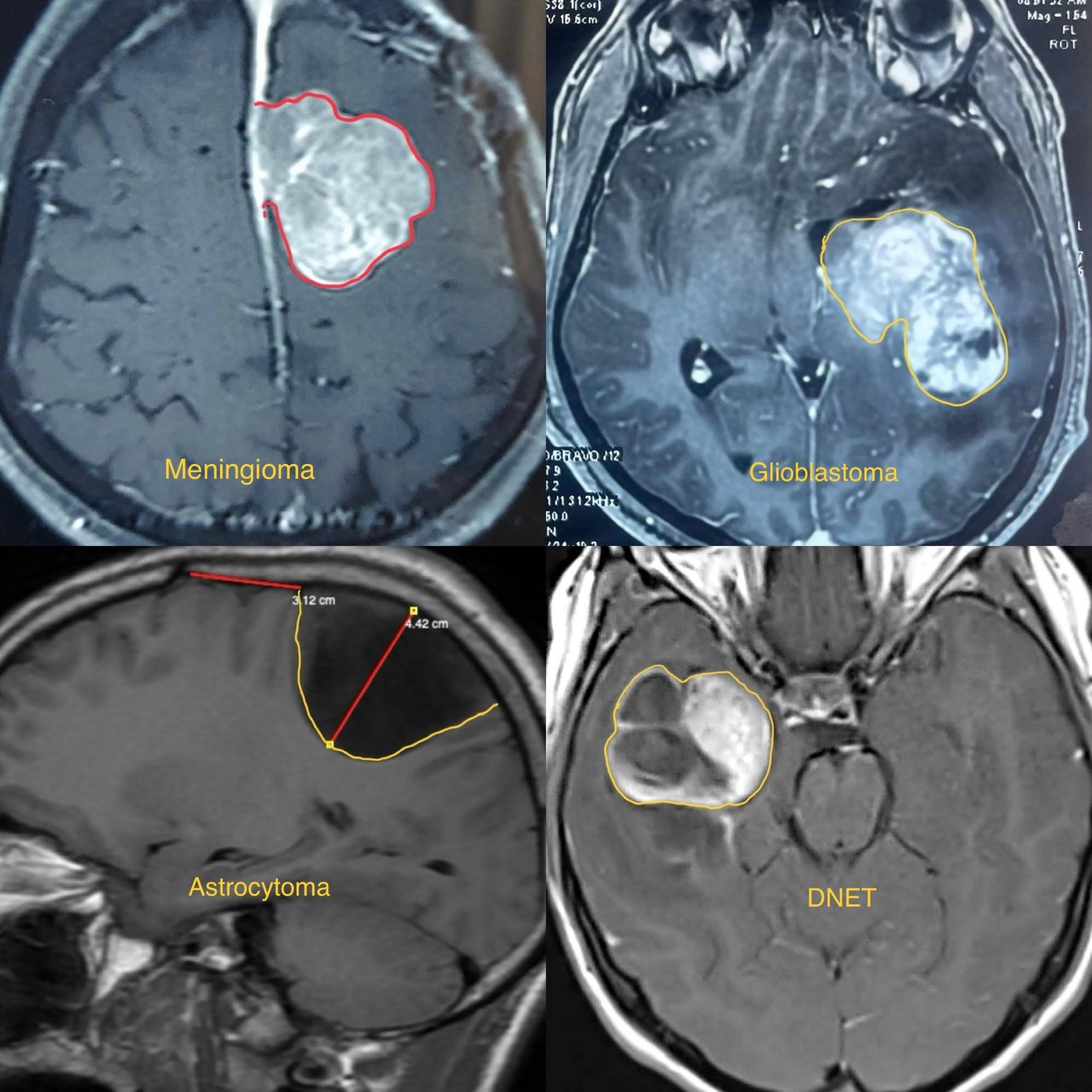
Brain Tumors
What is it?
Brain tumors are abnormal growths of cells within the brain. These tumors can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous), and they can originate from brain tissue itself (primary brain tumors) or spread to the brain from other parts of the body (metastatic brain tumors).
Symptoms:
- Symptoms of brain tumors can vary widely depending on the size, location, and type of tumor.
- Common symptoms may include headaches, seizures, changes in vision, difficulty with balance or coordination, cognitive changes, weakness or numbness in the limbs, and personality or behavior changes.
Primary Symptoms:
The primary symptoms that may indicate a brain tumor include:
- Headaches: Persistent or severe headaches, particularly in the morning or with changes in position, may indicate increased pressure within the skull.
- Seizures: Sudden, unexplained seizures may occur if the tumor irritates or compresses the brain tissue.
- Cognitive Changes: Difficulty with memory, concentration, or other cognitive functions may occur as the tumor affects brain function.
- Neurological Deficits: Weakness, numbness, or tingling in the arms or legs, changes in vision, or difficulty with speech or coordination may indicate compression of specific areas of the brain by the tumor.
Diagnosis/Treatment:
- Diagnosis typically involves a thorough neurological examination, medical history, imaging studies such as MRI or CT scans, and sometimes biopsy to determine the type and grade of the tumor.
- Treatment options vary depending on the type, size, location, and grade of the tumor but may include surgery to remove the tumor, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, or a combination of these treatments.
What to Expect After Surgery:
- After surgery for a brain tumor, patients can expect relief from symptoms caused by the tumor, such as headaches or neurological deficits.
- Recovery time varies depending on the extent of the surgery and the individual patient’s condition, but most patients can expect to gradually improve over several weeks to months.
- Rehabilitation, including physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and cognitive therapy, may be necessary to help regain function and independence.
Risk & Complications:
- As with any surgery, there are risks associated with procedures to treat brain tumors, including bleeding, infection, nerve injury, and complications related to anesthesia.
- Additionally, there may be a risk of complications specific to the location and type of tumor being treated, such as damage to nearby brain tissue, changes in cognitive function, or recurrence of the tumor.
- However, complications are relatively rare, and the benefits of surgery often outweigh the risks, particularly when the tumor is causing significant symptoms or affecting brain function. Early detection and treatment can improve outcomes and quality of life for patients with brain tumors.
Brain Treatments
About Dr. Bharat
Dr Bharat Shinde completed his M.Ch Neurosurgery from the National Institute Of Mental Health And Neurosciences (NIMHANS), Bangalore which is an institute of National importance.
