Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
What is it?
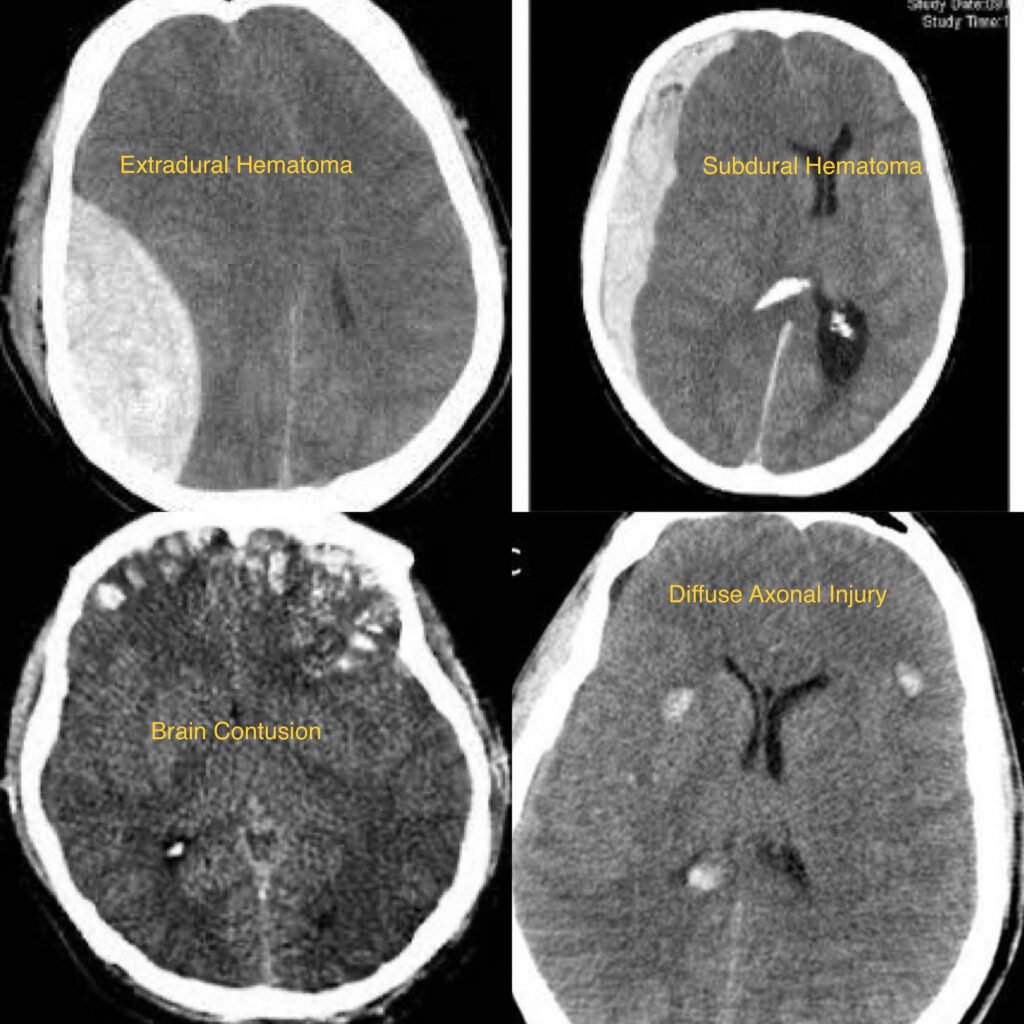
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) refers to damage to the brain caused by an external force, such as a blow, jolt, or penetrating injury to the head. TBIs can range from mild concussions to severe injuries resulting in long-term cognitive, physical, or emotional impairment.
Symptoms:
- Symptoms of TBI can vary widely depending on the severity and location of the injury.
- Common symptoms may include headache, confusion, dizziness, nausea or vomiting, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, memory problems, mood changes, and in severe cases, loss of consciousness.
Primary Symptoms:
The primary symptoms of TBI may include:
- Headache: Persistent or severe headache is a common symptom of TBI.
- Confusion: Disorientation, difficulty concentrating, and memory problems are common after a head injury.
- Nausea or Vomiting: Feeling sick to the stomach or vomiting may occur shortly after the injury.
- Loss of Consciousness: In severe cases of TBI, loss of consciousness may occur, ranging from a few seconds to hours or longer.
Diagnosis/Treatment:
- Diagnosis typically involves a thorough neurological examination, assessment of symptoms, and imaging studies such as CT scans or MRI to evaluate the extent of brain injury.
- Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the injury but may include rest, medication for pain or nausea, monitoring for changes in symptoms, and in severe cases, surgery to relieve pressure on the brain or repair skull fractures.
What to Expect After Surgery:
- After surgery for TBI, patients can expect a period of recovery, which may involve rehabilitation, physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and cognitive therapy.
- Recovery time varies depending on the severity of the injury and the individual patient’s response to treatment, but most patients can expect gradual improvement over weeks to months.
- It’s important to follow the healthcare provider’s recommendations for rest, activity restrictions, and rehabilitation to optimize recovery.
Risk & Complications:
- As with any surgery, there are risks associated with procedures to treat TBI, including infection, bleeding, nerve injury, and complications related to anesthesia.
- Additionally, there may be a risk of long-term complications such as cognitive impairment, mood disorders, seizures, and changes in behavior or personality.
- It’s important to closely monitor symptoms and follow up with healthcare providers to address any concerns and optimize recovery.
Brain Treatments
About Dr. Bharat
Dr Bharat Shinde completed his M.Ch Neurosurgery from the National Institute Of Mental Health And Neurosciences (NIMHANS), Bangalore which is an institute of National importance.
