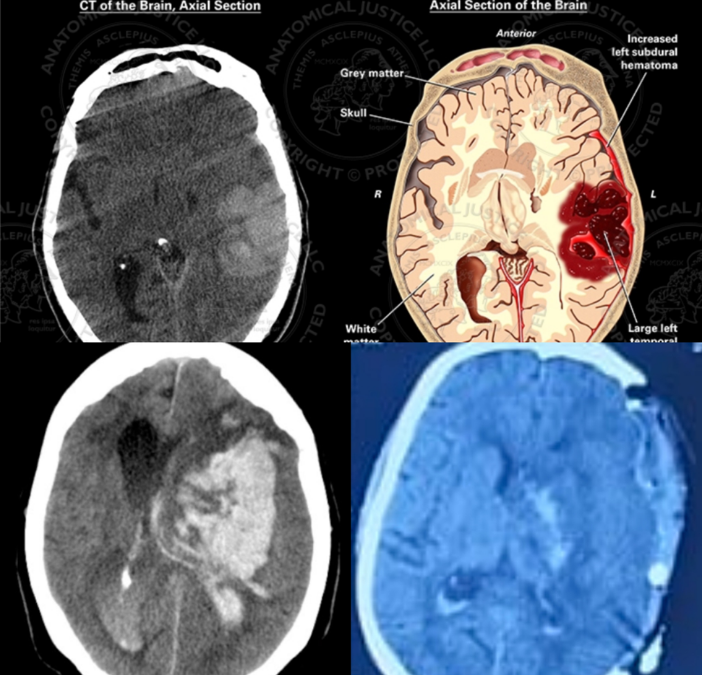
What is Intracranial Hematoma (ICH)?
An intracranial hematoma (ICH) occurs when blood vessels within the brain rupture, leading to the accumulation of blood in the skull. This condition can cause significant pressure on the brain, leading to serious complications. Intracranial hematomas are more commonly seen in older adults, particularly those with a history of high blood pressure (hypertension). Individuals who don’t manage their blood pressure well or are not compliant with medications are at higher risk. Additionally, patients on blood thinners (such as Ecosprin or Clopidogrel) are more prone to bleeding, which can be aggravated by uncontrolled hypertension.
What is the Role of Surgery in Treating ICH?
Surgical intervention is crucial for managing intracranial hematomas, especially in severe cases. Surgery is typically recommended when:
- Large Hematoma: When the blood clot volume exceeds 30 ml.
- Mass Effect: When there is a midline shift of more than 5 mm, which indicates that the pressure inside the skull is causing the brain to shift to one side.
- Low GCS (Glasgow Coma Scale): A very low GCS score (less than 8), suggesting that the patient is in a deep coma or unresponsive.
In these cases, a neurosurgeon in Thane may recommend surgery to alleviate pressure on the brain and prevent further damage.
How is ICH Surgery Performed?
The surgical procedure for intracranial hematoma involves the following steps:
- Craniotomy: A portion of the skull is temporarily removed to access the hematoma.
- Hematoma Removal: The accumulated blood is carefully removed to relieve the pressure on the brain.
- Skull Bone Preservation: The skull bone removed during surgery is generally kept in a sterile environment (either preserved outside the body or placed in the abdomen). The bone is replaced after the patient’s condition improves, usually within 3 months.
However, if high blood pressure persists post-surgery, the risk of rebleeding at the operative site remains. In some cases, additional surgery may be needed to reduce intracranial pressure further.
Can a Patient Fully Recover from an Intracranial Hematoma?
The recovery from intracranial hematoma depends on various factors:
- Preoperative Neurological Status: A patient’s GCS score before surgery is a significant predictor of recovery.
- Size and Location of the Hematoma: The site and size of the blood clot in the brain influence the extent of damage.
- Physical Rehabilitation: Many patients experience paralysis or weakness on one side of the body (hemiparesis) after the hematoma. However, with aggressive physiotherapy, there may be partial or full recovery of motor function over time.
Is Intracranial Hematoma Life-Threatening?
Yes, intracranial hematomas can be life-threatening. A large hematoma leads to a rapid increase in intracranial pressure, which can damage brain tissue and cause irreversible brain injury. Surgical intervention aims to reduce pressure rather than repair brain damage.
The prognosis of recovery varies and depends on:
- The size and location of the hematoma.
- Pre-existing health conditions (such as diabetes or hypertension).
- Postoperative complications.
- The age and overall health of the patient.
In some cases, especially with large hematomas, poor preoperative health, and postoperative complications, the condition may be fatal.
What Are the Possible Postoperative Complications?
After ICH surgery, patients are typically monitored in an intensive care unit (ICU) and may be placed on ventilator support to assist with breathing. Prolonged use of a ventilator increases the risk of ventilator-associated pneumonia, a serious lung infection that requires strong antibiotics.
Other potential complications include:
- Bedsores (from prolonged immobility in the ICU).
- Wound infections at the surgical site.
- Seizures, which may develop in the long term due to brain damage or scarring.
Why Choose a Neurosurgeon in Thane for ICH Treatment?
If you or a loved one is suffering from an intracranial hematoma and require expert medical intervention, seeking the guidance of an experienced neurosurgeon in Thane is crucial. A skilled neurosurgeon can assess the severity of the condition, provide timely surgical intervention, and offer comprehensive post-surgery care to improve recovery outcomes.